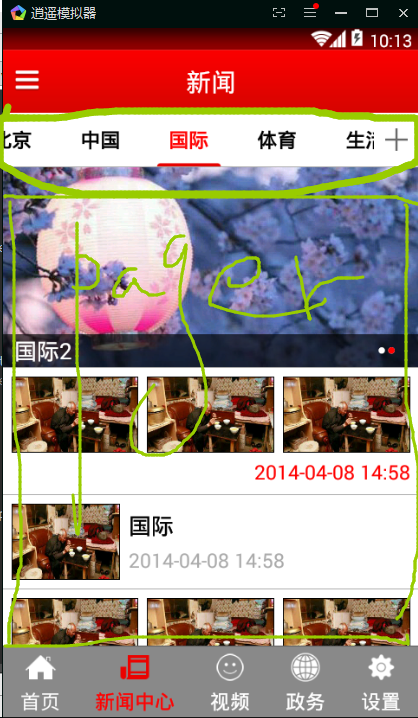
TabPagerIndicator使用
本文共 1433 字,大约阅读时间需要 4 分钟。
 1 注意/在清单文件中配置activity/theme=
1 注意/在清单文件中配置activity/theme=
android:theme="@style/Theme.PageIndicatorDefaults">
// 2 (adpter中添加getPageTitle)
2 (adpter中添加getPageTitle)
//1.给viewPager设置数据适配器 MyPagerAdapter myPagerAdapter = new MyPagerAdapter(); pager.setAdapter(myPagerAdapter); //2.指示器和viewPager进行绑定 indicator.setViewPager(pager);
3 重点(修改选中文字的颜色,背景) values/style/tabPageIndicator
values/style/tabPageIndicator
@android:color/transparent 为加背景,,不能用@null
<item name="vpiTabPageIndicatorStyle">@style/Widget.TabPageIndicator</item>//这里
</style>
<style name="Widget"> </style> <style name="Widget.TabPageIndicator" parent="Widget"> <item name="android:gravity">center</item><item name="android:background">@drawable/vpi__tab_indicator</item>//背景
<item name="android:paddingLeft">22dip</item> <item name="android:paddingRight">22dip</item> <item name="android:paddingTop">12dp</item> <item name="android:paddingBottom">12dp</item> <item name="android:textAppearance">@style/TextAppearance.TabPageIndicator</item> <item name="android:textSize">12sp</item> <item name="android:maxLines">1</item> </style> <style name="TextAppearance.TabPageIndicator" parent="Widget"> <item name="android:textStyle">bold</item><item name="android:textColor">@color/vpi__dark_theme</item>//文字颜色
</style> <style name="Widget.IconPageIndicator" parent="Widget"> <item name="android:layout_marginLeft">6dp</item> <item name="android:layout_marginRight">6dp</item> </style></resources>
你可能感兴趣的文章
NFS的常用挂载参数
查看>>
NFS网络文件系统
查看>>
NFS远程目录挂载
查看>>
nft文件传输_利用remoting实现文件传输-.NET教程,远程及网络应用
查看>>
NFV商用可行新华三vBRAS方案实践验证
查看>>
ng build --aot --prod生成文件报错
查看>>
ng 指令的自定义、使用
查看>>
ng6.1 新特性:滚回到之前的位置
查看>>
nghttp3使用指南
查看>>
Nginx
查看>>
nginx + etcd 动态负载均衡实践(一)—— 组件介绍
查看>>
nginx + etcd 动态负载均衡实践(三)—— 基于nginx-upsync-module实现
查看>>
nginx + etcd 动态负载均衡实践(二)—— 组件安装
查看>>
nginx + etcd 动态负载均衡实践(四)—— 基于confd实现
查看>>
Nginx + Spring Boot 实现负载均衡
查看>>
Nginx + Tomcat + SpringBoot 部署项目
查看>>
Nginx + uWSGI + Flask + Vhost
查看>>
Nginx - Header详解
查看>>
nginx - thinkphp 如何实现url的rewrite
查看>>
Nginx - 反向代理、负载均衡、动静分离、底层原理(案例实战分析)
查看>>